 :
:
For the
![]() case, let's see what happens if we
``precompute'' the characteristic polynomial using letters, by
writing
case, let's see what happens if we
``precompute'' the characteristic polynomial using letters, by
writing
 :
:
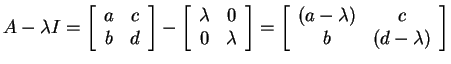 , so
, so
![]() .
.
Notice that the constant term is ![]() . The coefficient of
. The coefficient of
![]() is
is ![]() . The trace of a matrix means the sum
of the diagonal entries, so the coefficient of
. The trace of a matrix means the sum
of the diagonal entries, so the coefficient of ![]() is
minus the trace.
is
minus the trace.
Now you can see this fact:
Observation. If ![]() is
is
![]() , then
, then
![]() trace
trace![]() .
.
Now it becomes easy to write down the characteristic polynomials in the examples from the early sections of this handout:
For
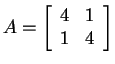 we get
we get
![]() trace
trace![]() .
.
For
 we get
we get
![]() trace
trace![]() .
.
For
 we get
we get
![]() trace
trace![]() .
.
This explains why all three examples had the same eigenvalues: All three had the same characteristic polynomial.
Problem
U-7. Invent two more
![]() matrices with
characteristic polynomial
matrices with
characteristic polynomial
![]() .
.