Now let's apply the ideas of the last sections in three dimensions:
(1) The three-point relational form of a plane in
R![]() is given by the equation
is given by the equation
![]() x
x![]()
![]()
![]() , where
, where
![]() x
x![$ ) =
{\left[\begin{array}{cccc}\ &P&\ &1\\ \ &Q&\ &1\\ \ &R&\ &1\\ \ &\mbox{\bf x}& \ &1\end{array}\right]}
$](img120.gif) .
.
(2)
![]() x
x![]() when
x
when
x![]() is in the
same relation to
is in the
same relation to ![]() that the origin is to
that the origin is to ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() , namely,
, namely, ![]() to
to ![]() to
to ![]() to
to ![]() is clockwise as seen from
x
is clockwise as seen from
x![]() .
.
(3) A line segment
![]() crosses the plane
given by an affine function
crosses the plane
given by an affine function ![]() if
if ![]() and
and
![]() are nonzero and have opposite signs; the crossing
point
are nonzero and have opposite signs; the crossing
point ![]() is given by
is given by ![]()
![]()
![]() ,
where
,
where ![]()
![]()
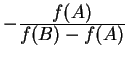 .
.